목차
1. 서론
2. 실험방법
2.1 사용분말
2.2 소결코아의 제조
3. 연구결과 및 고찰
3.1 분진을 첨가한 소결코아의 자기특성
3.2 분진을 첨가한 소결코아의 미세조직
4. 결론
2. 실험방법
2.1 사용분말
2.2 소결코아의 제조
3. 연구결과 및 고찰
3.1 분진을 첨가한 소결코아의 자기특성
3.2 분진을 첨가한 소결코아의 미세조직
4. 결론
본문내용
있음을 확인할 수 있다.
4. 결론
순철코아의 소결밀도와 자기특성에 미치는 STS 분진의 첨가량 및 소결온도의 영향을 조사한 결과 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
1) 소결온도가 증가할수록 소결체의 밀도 및 자기특성은 향상되었으며 1350 oC에 서 1시간 동안 소결한 경우 우수한 자기특성을 나타내었다.
2) 분진을 함유한 소결코아의 자기특성은, 분진의 첨가량이 증가할수록 열악해지 나, 한 예로 최고 10 wt.%의 분진첨가시 얻어진 직류특성은, 자속밀도(B15), 보 자력(Hc) 및 최대투자율(μmax)이 각각 9.8∼10.9 kG, 2.2∼2.3 Oe, 1950∼2050 인 비교적 양호한 값이었다.
3) 2)의 원인은, 소결코아 내부의 첨가된 분진은 복잡한 구조를 가지는 산화물로 순철보다 훨씬 낮은 1100∼1250 oC에서 용융되었고 소결과정에서 순철과 새 로운 화합물 혹은 개재물을 생성시키지 않고 단순히 순철과 혼합상태로 존재 하였기 때문이다.
4) STS 분진의 재활용가능량은 코아중량의 최대 10 wt.%로 추량된다.
5) 본 연구에서 얻어진 분진을 첨가한 소결코아는 자동차, DC 모터의 고정자 등 에 활용이 기대된다.
참 고 문 헌
1. 日本公開特許公報 昭 52-32809
2. 日本公開特許公報 昭 62-103343
3. 日本公開特許公報 平 2-57615
4. C.Lall : "Soft Magnetism", Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, New Jersey, U.S.A, 40(1992)
5. 김상원, 양충진, 박언병 : "STS공장 발생분진의 분리집진 기술", 연구보고서,
포항산업과학연구원(1996)
6. 李鐘南, 文仁炯 : "粉末冶金學", 光林社, 47(1994)
7. 김상원, 양충진 : "원심분무법 제조 분말로 제작된 Fe-79Ni-4Mo 소결코아의 자기특성", 한국자기학회지, 6(6), 388-396(1996)
8. C.Lall : "Soft Magnetism", Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, New Jersey, U.S.A, 80(1992)
9. K.S.Narsimhan : "Digest of Soft Magnetic Materials 96", Gorham/Intertech
Consulting, San Francisco, U.S.A(1996)
FIGURE CAPTION
Fig. 1 SEM micrographs showing the law Fe powder
Fig. 2 SEM micrograph showing the dusts and EDX spectrum from those
Fig. 3 Schematic flows indicating the fabrication process of sintered cores
Fig. 4 Sintering temperature dependency of AC magnetic properties
measured at the frequency of 60 Hz in an exciting field
of 15 Oe as a function of dusts content for the sintered cores
Fig. 5 Sintering temperature dependency of AC magnetic properties
measured at the frequency of 60 Hz in a magnetic induction
of 0.3 T as a function of dusts content for the sintered cores
Fig. 6 Optical micrographs of Fe-X wt.%dusts cores sintered at 1100 oC
for 1hr, (a) X=0, (b) X=5 and (c) X=10, respectively
Fig. 7 Optical micrographs of Fe-X wt.%dusts cores sintered at 1250 oC
for 1hr, (a) X=0, (b) X=5 and (c) X=10, respectively
Fig. 8 Optical micrographs of Fe-X wt.%dusts cores sintered at 1350 oC
for 1hr, (a) X=0, (b) X=5 and (c) X=10, respectively
Fig. 9 Shape of the cores made of only dusts, which was sintered
at various temperature, (a) as compacted, (b) 1100 oC, (c) 1250 oC
and (d) 1350 oC, respectively
Fig. 10 XRD patterns of melted dusts
Fig. 11 SEM micrograph showing the sintered body and EDX spectrum
from that
Fig. 12 Typical hysteresis curves measured with 60 Hz sinusoidal
current for the cores made of only dusts
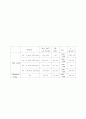
Table 1 Comparison of DC magnetic properties of obtained from the present
work and competitor's work for the sintered Fe cores
content
Bmax (kG)
(at 15 Oe)
Hc
(Oe)
μmax
ρ
(g/cm3)
This work
Fe + 3 wt.% STS dust
11.4∼13.0
2.0
2370∼
2500
7.35∼7.4
Fe + 5 wt.% STS dust
11.0∼12.7
2.0∼2.1
2350∼
2450
7.2∼7.3
Fe + 7 wt.% STS dust
10.7∼11.9
2.1∼2.2
1980∼
2100
7.15
Fe + 10 wt.% STS dust
9.8∼10.9
2.2∼2.3
1950∼
2050
6.9∼7.0
Hoganas
Corp.
Fe
10∼13
1.5∼2.5
1800∼
3500
6.8∼7.2
4. 결론
순철코아의 소결밀도와 자기특성에 미치는 STS 분진의 첨가량 및 소결온도의 영향을 조사한 결과 다음과 같은 결론을 얻었다.
1) 소결온도가 증가할수록 소결체의 밀도 및 자기특성은 향상되었으며 1350 oC에 서 1시간 동안 소결한 경우 우수한 자기특성을 나타내었다.
2) 분진을 함유한 소결코아의 자기특성은, 분진의 첨가량이 증가할수록 열악해지 나, 한 예로 최고 10 wt.%의 분진첨가시 얻어진 직류특성은, 자속밀도(B15), 보 자력(Hc) 및 최대투자율(μmax)이 각각 9.8∼10.9 kG, 2.2∼2.3 Oe, 1950∼2050 인 비교적 양호한 값이었다.
3) 2)의 원인은, 소결코아 내부의 첨가된 분진은 복잡한 구조를 가지는 산화물로 순철보다 훨씬 낮은 1100∼1250 oC에서 용융되었고 소결과정에서 순철과 새 로운 화합물 혹은 개재물을 생성시키지 않고 단순히 순철과 혼합상태로 존재 하였기 때문이다.
4) STS 분진의 재활용가능량은 코아중량의 최대 10 wt.%로 추량된다.
5) 본 연구에서 얻어진 분진을 첨가한 소결코아는 자동차, DC 모터의 고정자 등 에 활용이 기대된다.
참 고 문 헌
1. 日本公開特許公報 昭 52-32809
2. 日本公開特許公報 昭 62-103343
3. 日本公開特許公報 平 2-57615
4. C.Lall : "Soft Magnetism", Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, New Jersey, U.S.A, 40(1992)
5. 김상원, 양충진, 박언병 : "STS공장 발생분진의 분리집진 기술", 연구보고서,
포항산업과학연구원(1996)
6. 李鐘南, 文仁炯 : "粉末冶金學", 光林社, 47(1994)
7. 김상원, 양충진 : "원심분무법 제조 분말로 제작된 Fe-79Ni-4Mo 소결코아의 자기특성", 한국자기학회지, 6(6), 388-396(1996)
8. C.Lall : "Soft Magnetism", Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princeton, New Jersey, U.S.A, 80(1992)
9. K.S.Narsimhan : "Digest of Soft Magnetic Materials 96", Gorham/Intertech
Consulting, San Francisco, U.S.A(1996)
FIGURE CAPTION
Fig. 1 SEM micrographs showing the law Fe powder
Fig. 2 SEM micrograph showing the dusts and EDX spectrum from those
Fig. 3 Schematic flows indicating the fabrication process of sintered cores
Fig. 4 Sintering temperature dependency of AC magnetic properties
measured at the frequency of 60 Hz in an exciting field
of 15 Oe as a function of dusts content for the sintered cores
Fig. 5 Sintering temperature dependency of AC magnetic properties
measured at the frequency of 60 Hz in a magnetic induction
of 0.3 T as a function of dusts content for the sintered cores
Fig. 6 Optical micrographs of Fe-X wt.%dusts cores sintered at 1100 oC
for 1hr, (a) X=0, (b) X=5 and (c) X=10, respectively
Fig. 7 Optical micrographs of Fe-X wt.%dusts cores sintered at 1250 oC
for 1hr, (a) X=0, (b) X=5 and (c) X=10, respectively
Fig. 8 Optical micrographs of Fe-X wt.%dusts cores sintered at 1350 oC
for 1hr, (a) X=0, (b) X=5 and (c) X=10, respectively
Fig. 9 Shape of the cores made of only dusts, which was sintered
at various temperature, (a) as compacted, (b) 1100 oC, (c) 1250 oC
and (d) 1350 oC, respectively
Fig. 10 XRD patterns of melted dusts
Fig. 11 SEM micrograph showing the sintered body and EDX spectrum
from that
Fig. 12 Typical hysteresis curves measured with 60 Hz sinusoidal
current for the cores made of only dusts
Table 1 Comparison of DC magnetic properties of obtained from the present
work and competitor's work for the sintered Fe cores
content
Bmax (kG)
(at 15 Oe)
Hc
(Oe)
μmax
ρ
(g/cm3)
This work
Fe + 3 wt.% STS dust
11.4∼13.0
2.0
2370∼
2500
7.35∼7.4
Fe + 5 wt.% STS dust
11.0∼12.7
2.0∼2.1
2350∼
2450
7.2∼7.3
Fe + 7 wt.% STS dust
10.7∼11.9
2.1∼2.2
1980∼
2100
7.15
Fe + 10 wt.% STS dust
9.8∼10.9
2.2∼2.3
1950∼
2050
6.9∼7.0
Hoganas
Corp.
Fe
10∼13
1.5∼2.5
1800∼
3500
6.8∼7.2