목차
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1 Experiment Instrumental System
2.2 Materials
2.3 Methods and Conditions of Experiment
3. Analysis Method of Degradation and Reduction Degree
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
2. Experimental
2.1 Experiment Instrumental System
2.2 Materials
2.3 Methods and Conditions of Experiment
3. Analysis Method of Degradation and Reduction Degree
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
본문내용
, Butterworth -Heinemann, Boston, (1991), 68
(18) Daizo Kunii and Octave Levenspiel : Fluidization Engineering, John Wiley & Sons, New York, (1962), 74
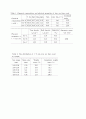
Table 1. Chemical compositions and physical properties of iron ore fines used.
Table 2. Size distribution of 1∼5 mm iron ore fines used as sample.
Table 3. Experimental conditions.
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of a fluidized-bed apparatus.
Fig. 2. Size distributions of iron ore fines before and after the cold fluidization.
Fig. 3. Effect of ore type on the size distribution of iron ore fines.
Fig. 4. Variation of the size distribution of iron ore fines with reaction time.
Fig. 5. Variation of reduction degree with time during the fluidized-bed reduction.
Fig. 6. Effect of temperature on the size distribution of iron ore fines.
Fig. 7. Effect of superficial gas velocity on the size distribution of iron ore fines.
Fig. 8. Effect of superficial gas velocity on the elutriation loss of iron ore fines.
Fig. 9. Effect of gas composition on the size distribution of iron ore fines.
Fig. 10. Size distributions of iron ore fines before and after the hot fluidization
under nitrogen atmosphere.
Fig. 11. Size distributions of iron ore fines before and after the cold fluidization
under nitrogen atmosphere.
Fig. 12. Comparison of size distributions for the cold and hot fluidization of Ore-A.
Fig. 13. Comparison of size distributions for the cold and hot fluidization of Ore-B.
Fig. 14. Variation in solid holdup in vertical direction of reactor during
the fluidized-bed reduction of iron ore fines.
Fig. 15. Variation in total weight and pressure drop in reactor during
the fluidized-bed reduction of iron ore fines.
Fig. 16. Size distributions of iron ore fines in reactor, cyclone, collector and filter before and after reduction.
Table 1. Chemical compositions and physical properties of iron ore fines used.
Chemical
compositions
(
wt``%``
)
T. Fe
FeO
SiO2
Al2O3
TiO2
CaO, Mn, P, S
Combined
water
Ore-A
63.49
0.37
4.32
2.33
0.11
bal.
3.55
Ore-B
59.10
0.51
4.63
1.21
0.05
bal.
8.46
Ore-C
65.20
0.49
4.18
1.54
0.46
bal.
2.83
Physical
properties of
1∼5 mm ores
True density
(
g/cm^3`
)
Bulk density
(
g/cm^3`
)
Sphericity
(
varphi _p
)
Harmonic mean
size ( m)
Ore-A
4.50
2.37
0.73
2260
Ore-B
4.43
2.21
0.61
Ore-C
4.62
2.03
0.45
Table 2. Size distribution of 1∼5 mm iron ore fines used
as sample.
Size range
(mm)
Mean size
(mm)
Weight
(mass %)
Cumulative weight
(mass %)
1.00-2.00
2.00-2.86
2.86-3.36
3.36-4.00
4.00-4.75
1.50
2.43
3.11
3.68
4.38
36.5
18.8
11.7
19.3
13.7
36.5
55.3
67.0
86.3
100.0
Table 3. Experimental conditions.
Variables
Conditions
Ore type
Ore-A(Fe2O3), Ore-B(Fe2O3·H2O)
Ore-C(Fe2O3)
Particle size
1∼5 mm
Temperature
Room temperature, 710∼890 ℃
Gas atmosphere and
composition
N2(100)
Mixing gas, (vol. %)
MG1 : CO(50), CO2(20), H2(25), Ar(5)
MG2 : CO(65), CO2(5), H2(25), Ar(5)
Fluidization time
5∼50 min
Superficial gas velocity
2.5 Nm/s (cold), 3.5∼4.9 m/s (hot)
Ore weight
1000∼6000 g
Pressure
1.15 atm
(18) Daizo Kunii and Octave Levenspiel : Fluidization Engineering, John Wiley & Sons, New York, (1962), 74
Table 1. Chemical compositions and physical properties of iron ore fines used.
Table 2. Size distribution of 1∼5 mm iron ore fines used as sample.
Table 3. Experimental conditions.
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of a fluidized-bed apparatus.
Fig. 2. Size distributions of iron ore fines before and after the cold fluidization.
Fig. 3. Effect of ore type on the size distribution of iron ore fines.
Fig. 4. Variation of the size distribution of iron ore fines with reaction time.
Fig. 5. Variation of reduction degree with time during the fluidized-bed reduction.
Fig. 6. Effect of temperature on the size distribution of iron ore fines.
Fig. 7. Effect of superficial gas velocity on the size distribution of iron ore fines.
Fig. 8. Effect of superficial gas velocity on the elutriation loss of iron ore fines.
Fig. 9. Effect of gas composition on the size distribution of iron ore fines.
Fig. 10. Size distributions of iron ore fines before and after the hot fluidization
under nitrogen atmosphere.
Fig. 11. Size distributions of iron ore fines before and after the cold fluidization
under nitrogen atmosphere.
Fig. 12. Comparison of size distributions for the cold and hot fluidization of Ore-A.
Fig. 13. Comparison of size distributions for the cold and hot fluidization of Ore-B.
Fig. 14. Variation in solid holdup in vertical direction of reactor during
the fluidized-bed reduction of iron ore fines.
Fig. 15. Variation in total weight and pressure drop in reactor during
the fluidized-bed reduction of iron ore fines.
Fig. 16. Size distributions of iron ore fines in reactor, cyclone, collector and filter before and after reduction.
Table 1. Chemical compositions and physical properties of iron ore fines used.
Chemical
compositions
(
wt``%``
)
T. Fe
FeO
SiO2
Al2O3
TiO2
CaO, Mn, P, S
Combined
water
Ore-A
63.49
0.37
4.32
2.33
0.11
bal.
3.55
Ore-B
59.10
0.51
4.63
1.21
0.05
bal.
8.46
Ore-C
65.20
0.49
4.18
1.54
0.46
bal.
2.83
Physical
properties of
1∼5 mm ores
True density
(
g/cm^3`
)
Bulk density
(
g/cm^3`
)
Sphericity
(
varphi _p
)
Harmonic mean
size ( m)
Ore-A
4.50
2.37
0.73
2260
Ore-B
4.43
2.21
0.61
Ore-C
4.62
2.03
0.45
Table 2. Size distribution of 1∼5 mm iron ore fines used
as sample.
Size range
(mm)
Mean size
(mm)
Weight
(mass %)
Cumulative weight
(mass %)
1.00-2.00
2.00-2.86
2.86-3.36
3.36-4.00
4.00-4.75
1.50
2.43
3.11
3.68
4.38
36.5
18.8
11.7
19.3
13.7
36.5
55.3
67.0
86.3
100.0
Table 3. Experimental conditions.
Variables
Conditions
Ore type
Ore-A(Fe2O3), Ore-B(Fe2O3·H2O)
Ore-C(Fe2O3)
Particle size
1∼5 mm
Temperature
Room temperature, 710∼890 ℃
Gas atmosphere and
composition
N2(100)
Mixing gas, (vol. %)
MG1 : CO(50), CO2(20), H2(25), Ar(5)
MG2 : CO(65), CO2(5), H2(25), Ar(5)
Fluidization time
5∼50 min
Superficial gas velocity
2.5 Nm/s (cold), 3.5∼4.9 m/s (hot)
Ore weight
1000∼6000 g
Pressure
1.15 atm
추천자료
 생물의 특성과 세포의 연구
생물의 특성과 세포의 연구 [뉴미디어][뉴미디어규제][뉴미디어정책][미디어][뉴미디어 등장배경][뉴미디어 특성]뉴미디...
[뉴미디어][뉴미디어규제][뉴미디어정책][미디어][뉴미디어 등장배경][뉴미디어 특성]뉴미디... [법과 도덕][법][도덕][법과 도덕의 관계][법과 도덕의 특성][법과 도덕의 구별][법과 도덕의...
[법과 도덕][법][도덕][법과 도덕의 관계][법과 도덕의 특성][법과 도덕의 구별][법과 도덕의... [인간발달][인간발달 개념][인간발달 원리][인간발달 단계][인간발달단계에 따른 발달특성][...
[인간발달][인간발달 개념][인간발달 원리][인간발달 단계][인간발달단계에 따른 발달특성][... 학습자의 특성
학습자의 특성 포스트모더니즘의 특성, 포스트모더니즘의 등장배경, 포스트모더니즘의 중요성, 포스트모더니...
포스트모더니즘의 특성, 포스트모더니즘의 등장배경, 포스트모더니즘의 중요성, 포스트모더니... 슬기로운생활과의 특성, 슬기로운생활과의 목표, 슬기로운생활과의 기본 방향, 슬기로운생활...
슬기로운생활과의 특성, 슬기로운생활과의 목표, 슬기로운생활과의 기본 방향, 슬기로운생활... 아동의 특성, 욕구와 문제, 아동을 위한 자원봉사활동의 필요성
아동의 특성, 욕구와 문제, 아동을 위한 자원봉사활동의 필요성 정신지체아의 특성, 정신지체아의 놀이, 정신지체아의 식습관형성지도, 정신지체아의 자아개...
정신지체아의 특성, 정신지체아의 놀이, 정신지체아의 식습관형성지도, 정신지체아의 자아개... 인간발달의 특성과 영아기, 유아기의 신체, 인지, 언어, 정서, 사회성 발달 특징에 대해 설명...
인간발달의 특성과 영아기, 유아기의 신체, 인지, 언어, 정서, 사회성 발달 특징에 대해 설명... 집단의 특성과 유형
집단의 특성과 유형 [촌락, 마을, 촌락(마을) 발달, 촌락(마을) 특성, 사원촌락]촌락(마을)의 발달, 촌락(마을)의...
[촌락, 마을, 촌락(마을) 발달, 촌락(마을) 특성, 사원촌락]촌락(마을)의 발달, 촌락(마을)의... [건축학] 철골구조 (鐵骨構造 / steel structure) (철골구조의 정의, 철골구조의 장단점, 강...
[건축학] 철골구조 (鐵骨構造 / steel structure) (철골구조의 정의, 철골구조의 장단점, 강...