
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20
-
21
-
22
-
23
-
24
-
25
-
26
-
27
-
28
-
29
-
30
-
31
-
32
-
33
-
34
-
35
-
36
-
37
-
38
-
39
-
40
-
41


목차
目 次
I, 序 論
1.연구의배경 및 필요성
2. 연구의 목적
3. 연구의 대상 및 방법
1) 연구대상
2) 설문조사기간
3) 설문방법
4) 조사도구 및 내용
II. 理論的 背景
1. 노인의 개념 및 특성
2. 노인인구의 현황과 노인의료문제의 성격
1) 노인인구의 현황
2) 노인의료문제의 성격
3. 노령인구의 의료수요와 공급
1) 노인의료의 수요
2) 노인의료의 공급
III.硏究結果 分析
1. 연구 대상자의 일반적 특성
1) 성별, 연령별 특성
2) 질병상태
2. 보건소의 이용현황
1) 교통수단 및 의사결정자
2) 다른 의료기관과 관련된 사항
가.방문의료기관
나.변경이유
3. 의료기관에 대한 인식
1) 진료 부작용 경험
2) 부작용경험 의료기관
3) 의료기관에 대한 태도
4) 의료기관결정시 고려사항
4. 건강관리
1) 주관적 건강상태 및 영양
2) 운동
3) 영양제 및 건강식품
4) 건강검진
5) 건강관련 정보원
IV. 考察 및 運營方案 摸索
1. 고찰
1) 노령인구의 건강상태
2) 노령인구의 건강관리
3) 보건소의 노인보건사업 운영현황
2. 운영방안 모색
1) 보건소의 노인보건 사업 현황
2) 노인 보건사업 운영 방안
V. 결 론
참고문헌
설문지
영문초록
표 목 차
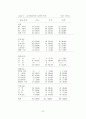
<1-1> 인구구조의 변동추이
<1-2> 우리나라의 평균수명의 추이
<1-3> 우리나라의 총 부양비와 노인부양비의 추이
<1-4> 1992년 노인의 암 입원 진료실적
<1-5> 시군부별 의료기관 및 병상분포 상황
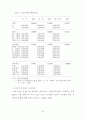
<표2-1> 연구대상자의 일반적 특성
<표2-2> 연구대상자의 질병상태
<표2-3> 연구대상자의 보건소 이용에 관한 사항
<표2-4> 다른 의료기관 방문자에 관한 사항
<표2-5> 의료기관 변경이유
<표2-6-1> 질병의 부작용 경험
<표2-6-2> 질병의 부작용 경험 의료기관
<표2-7> 의료기관에 대한 인식태도
<표2-8> 의료기관 결정시 고려사항
<표2-9> 주관적 건강상태
<표2-10> 운동의 빈도
<표2-11> 영양제 및 건강식품 섭취
<표2-12> 건강검진
<표2-13> 건강관련 정보원
<표3-1> 노인들의 건강관리방법
<표3-2> 연령별 건강검진 참여율 및 결과
* 설문지 첨부
I, 序 論
1.연구의배경 및 필요성
2. 연구의 목적
3. 연구의 대상 및 방법
1) 연구대상
2) 설문조사기간
3) 설문방법
4) 조사도구 및 내용
II. 理論的 背景
1. 노인의 개념 및 특성
2. 노인인구의 현황과 노인의료문제의 성격
1) 노인인구의 현황
2) 노인의료문제의 성격
3. 노령인구의 의료수요와 공급
1) 노인의료의 수요
2) 노인의료의 공급
III.硏究結果 分析
1. 연구 대상자의 일반적 특성
1) 성별, 연령별 특성
2) 질병상태
2. 보건소의 이용현황
1) 교통수단 및 의사결정자
2) 다른 의료기관과 관련된 사항
가.방문의료기관
나.변경이유
3. 의료기관에 대한 인식
1) 진료 부작용 경험
2) 부작용경험 의료기관
3) 의료기관에 대한 태도
4) 의료기관결정시 고려사항
4. 건강관리
1) 주관적 건강상태 및 영양
2) 운동
3) 영양제 및 건강식품
4) 건강검진
5) 건강관련 정보원
IV. 考察 및 運營方案 摸索
1. 고찰
1) 노령인구의 건강상태
2) 노령인구의 건강관리
3) 보건소의 노인보건사업 운영현황
2. 운영방안 모색
1) 보건소의 노인보건 사업 현황
2) 노인 보건사업 운영 방안
V. 결 론
참고문헌
설문지
영문초록
표 목 차
<1-1> 인구구조의 변동추이
<1-2> 우리나라의 평균수명의 추이
<1-3> 우리나라의 총 부양비와 노인부양비의 추이
<1-4> 1992년 노인의 암 입원 진료실적
<1-5> 시군부별 의료기관 및 병상분포 상황
<표2-1> 연구대상자의 일반적 특성
<표2-2> 연구대상자의 질병상태
<표2-3> 연구대상자의 보건소 이용에 관한 사항
<표2-4> 다른 의료기관 방문자에 관한 사항
<표2-5> 의료기관 변경이유
<표2-6-1> 질병의 부작용 경험
<표2-6-2> 질병의 부작용 경험 의료기관
<표2-7> 의료기관에 대한 인식태도
<표2-8> 의료기관 결정시 고려사항
<표2-9> 주관적 건강상태
<표2-10> 운동의 빈도
<표2-11> 영양제 및 건강식품 섭취
<표2-12> 건강검진
<표2-13> 건강관련 정보원
<표3-1> 노인들의 건강관리방법
<표3-2> 연령별 건강검진 참여율 및 결과
* 설문지 첨부
본문내용
themselves, whereas others obtained advice from neighbors and friends, which accounted for 21.9% and 11.2 %, respectively.
4) Before visiting the health center, 70.6 % of the aged had taken medical care at other medical facilities. Among them, 33.3 % changed to the public heath center because of financial reason, 28.8 % due to ineffectiveness of therapy and location of medical facilities.
5) Among the aged who previously visited other medical facilities, 7.5 % were not satisfied with medical treatment received.
6) Regarding the opinion on the other medical facilities, different opinions were hold by age, sex, and educationional level. Both men and women believed that general hospital provided most effective treatment. The older the age and the higher the education, the stronger this prejudice was. Especially, this group of people gave low score to drug store but high score to hospital.
7) When the aged selected medical facilities, 31.2 % made a decision for the diseases they suffered from, 32.6 % for financial reason, 17.1 % for the location of medical facilities.
8) On their own-perceived self-estimated heath condition, more women than men thought negatively, and this was more true among the older group. In case of their present nutritional condition, similar tendency appeared. It also shows that the more pocket money women spent, the less points were given to their nutritional condition.
9) 21.9 % of the aged did exercise regularly but 38.5 % of them never. It shows that 26.7 % took nutrition stuffs and healthy food.
10) During the past three years, 57.3 % of the aged had not taken any health examination, while 38.5 %, 5.9 %, and 5.4 %, had taken once, twice, and three times, respectively.
11) The aged obtained health-related information mainly from TV/radio (56.7 %), while 20.3 % from neighbors. The group who never get any health-related information occupied 12.3 %.
From these results, to cope with the health needs of the aged and prepare a corresponding policy for managing health problem of the aged, following directions in systematic adjustment of the policy for the aged is proposed:
First, to play an important role in coping with the health need of the aged, local health centers should provide more various attractive services to the aged.
Second, the mobile medical services should be more active, specially in undeveloped regions that are far from medical facilities. More branches of public health centers should be considered to give close and convenient medical service to the aged.
Third, in order to meet the needs of the aged, the number of medical personnel in public health centers should be increased.
Finally, to instruct self-management of their health of the aged, health center should provide sufficient health-related information and build facilities like physical-therapy rooms and sports rooms for the aged.
__________________________________________________________
Key words: the aged, health need, satisfaction of medical need.
4) Before visiting the health center, 70.6 % of the aged had taken medical care at other medical facilities. Among them, 33.3 % changed to the public heath center because of financial reason, 28.8 % due to ineffectiveness of therapy and location of medical facilities.
5) Among the aged who previously visited other medical facilities, 7.5 % were not satisfied with medical treatment received.
6) Regarding the opinion on the other medical facilities, different opinions were hold by age, sex, and educationional level. Both men and women believed that general hospital provided most effective treatment. The older the age and the higher the education, the stronger this prejudice was. Especially, this group of people gave low score to drug store but high score to hospital.
7) When the aged selected medical facilities, 31.2 % made a decision for the diseases they suffered from, 32.6 % for financial reason, 17.1 % for the location of medical facilities.
8) On their own-perceived self-estimated heath condition, more women than men thought negatively, and this was more true among the older group. In case of their present nutritional condition, similar tendency appeared. It also shows that the more pocket money women spent, the less points were given to their nutritional condition.
9) 21.9 % of the aged did exercise regularly but 38.5 % of them never. It shows that 26.7 % took nutrition stuffs and healthy food.
10) During the past three years, 57.3 % of the aged had not taken any health examination, while 38.5 %, 5.9 %, and 5.4 %, had taken once, twice, and three times, respectively.
11) The aged obtained health-related information mainly from TV/radio (56.7 %), while 20.3 % from neighbors. The group who never get any health-related information occupied 12.3 %.
From these results, to cope with the health needs of the aged and prepare a corresponding policy for managing health problem of the aged, following directions in systematic adjustment of the policy for the aged is proposed:
First, to play an important role in coping with the health need of the aged, local health centers should provide more various attractive services to the aged.
Second, the mobile medical services should be more active, specially in undeveloped regions that are far from medical facilities. More branches of public health centers should be considered to give close and convenient medical service to the aged.
Third, in order to meet the needs of the aged, the number of medical personnel in public health centers should be increased.
Finally, to instruct self-management of their health of the aged, health center should provide sufficient health-related information and build facilities like physical-therapy rooms and sports rooms for the aged.
__________________________________________________________
Key words: the aged, health need, satisfaction of medical need.
추천자료
 건강관리사업-가정간호, 일차건강관리, 건강증진, managed care
건강관리사업-가정간호, 일차건강관리, 건강증진, managed care [의료보험제도][건강보험제도][국민건강보험제도][국민건강보험정책]의료보험제도, 건강보험...
[의료보험제도][건강보험제도][국민건강보험제도][국민건강보험정책]의료보험제도, 건강보험... [국민건강보험][국민건강보험제도][건강보험제도]국민건강보험의 연혁, 국민건강보험의 현황...
[국민건강보험][국민건강보험제도][건강보험제도]국민건강보험의 연혁, 국민건강보험의 현황... [체력][체력 정의][체력 요소][체력과 건강][체력과 운동][체력과 체력측정][체력 강화 방안]...
[체력][체력 정의][체력 요소][체력과 건강][체력과 운동][체력과 체력측정][체력 강화 방안]... [노인건강 방안] 노인건강의 실태, 노인 복지제도, 노인 건강관련 제도 분석 및 문제점과 개...
[노인건강 방안] 노인건강의 실태, 노인 복지제도, 노인 건강관련 제도 분석 및 문제점과 개... 건강가정에 대한 이론적 접근에 있어서 생태학적 관점이 건강가정에 미치는 중요요인에 대하...
건강가정에 대한 이론적 접근에 있어서 생태학적 관점이 건강가정에 미치는 중요요인에 대하... [건강증진론 A형] 우리나라 국민건강증진종합계획 2020의 기본모형을 사업분야(과제), 목표,...
[건강증진론 A형] 우리나라 국민건강증진종합계획 2020의 기본모형을 사업분야(과제), 목표,... [아동건강교육4공통]3~5세 누리과정 건강교육부분과 표준보육과정 건강교육과정 설명 & ...
[아동건강교육4공통]3~5세 누리과정 건강교육부분과 표준보육과정 건강교육과정 설명 & ... [생활과건강] 건강한 생활양식 중 관련된 내용을 상세히 기술. 제시한 내용 각각에 대한 효과...
[생활과건강] 건강한 생활양식 중 관련된 내용을 상세히 기술. 제시한 내용 각각에 대한 효과... 건강증진론) 제4차 국민건강증진계획(Health Plan 2020)의 중점과제인 노인건강의 지표별 목...
건강증진론) 제4차 국민건강증진계획(Health Plan 2020)의 중점과제인 노인건강의 지표별 목... 정신건강증진, 위기간호, 정신질환예방, 위기중재, 위기간호사정, 정신건강증진모형, 정신건...
정신건강증진, 위기간호, 정신질환예방, 위기중재, 위기간호사정, 정신건강증진모형, 정신건... 건강불평등(사회계층에 따른 건강불평등, 건강불평등에 대한 대응 및 중재방법)
건강불평등(사회계층에 따른 건강불평등, 건강불평등에 대한 대응 및 중재방법) 건강기능식품 현황과 문제점 및 건강기능식품 발전방안
건강기능식품 현황과 문제점 및 건강기능식품 발전방안 [생활과건강] 건강한 생활양식은 개인의 건강과 행복을 위해 매우 중요합니다 1) 자신이 수행...
[생활과건강] 건강한 생활양식은 개인의 건강과 행복을 위해 매우 중요합니다 1) 자신이 수행...

























































소개글