본문내용
lass Complex
{
friend Complex operator+(const Complex& x, const Complex& y);
friend Complex operator-(const Complex& x, const Complex& y);
friend Complex operator*(const Complex& x, const Complex& y);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Complex& c);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& i, const Complex& c);
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
Complex()
{
real = 0;
imag = 0;
}
Complex(double a, double b)
{
real = a;
imag = b;
}
~Complex(){}
double getReal() {return(real); }
double getImag() {return(imag); }
void print() {cout << real << " + " << imag << "i" << endl; }
};
Complex operator+(const Complex& x, const Complex& y)
{
Complex result;
result.real = x.real + y.real;
result.imag = x.imag + y.imag;
return result;
}
Complex operator-(const Complex& x, const Complex& y)
{
Complex result;
result.real = x.real - y.real;
result.imag = x.imag - y.imag;
return result;
}
Complex operator*(const Complex& x, const Complex& y)
{
Complex result;
result.real = x.real * y.real;
result.imag = x.imag * y.imag;
return result;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Complex& c)
{
os<< c.real << " + " << c.imag << "i" << endl;
return os;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, const Complex& c)
{
is>>(double)c.real>>(double)c.imag;
return is;
}
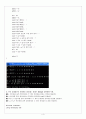
int main(void)
{
Complex x(2, 3), y(4, 6), z;
cout << "첫번째 복소수 x: ";
x.print();
cout << "두번째 복소수 y: ";
y.print();
z = x + y;
cout << "x + y = ";
z.print();
z = x - y;
cout << "x - y = ";
z.print();
z = x * y;
cout << "x * y = ";
z.print();
cout << "cout< ";
cout< ";
cin>>z;
cout<
}
9. [] 연산자도 중복이 가능하다.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class SymbolTable{
private:
string key[10];
int value[10];
int total;
public:
SymbolTable(){
for(int i=0; i< 10 ; i++){
key[i]="";
value[i] = 0;
total = 0;
}
}
void add(string key, int value)
{
for(int i=0; i< 10 ; i++){
if(this->value[i] == 0){
this->key[i] = key;
this->value[i] = value;
total++;
break;
}
}
}
void del(string key){
for(int i=0; i< 10; i++){
if( this->key[i] == key){
this->key[i]="";
this->value[i] = 0;
total--;
break;
}
}
}
int operator[](string key){
for(int i=0; i < 10; i++){
if( this->key[i] == key){
return this->value[i];
}
}
return -1;
}
};
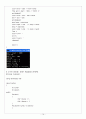
int main()
{
SymbolTable table;
table.add("house", 100);
table.add("mouse", 200);
table.add("korea", 300);
table.del("mouse");
cout<< table["house"] << endl;
return 0;
}
10. 직원을 나타내는 Employee 클래스의 객체를 정수형으로 형변환하면 월급을 반환하도록 Employee 클래스 안에 형변환 함수를 중복 정의하라.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Employee{
private:
string name;
int salary;
public:
Employee(){
name="Unknown";
salary = 0;
};
Employee(string name, int salary)
{
this->name = name;
this->salary = salary;
}
operator int() const
{
return salary;
}
void display()
{
cout<<"Name : "<
};
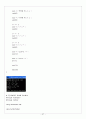
int main()
{
Employee e("홍길동", 100);
int salary = (int) e; // salary에 100이 저장된다
e.display();
cout<<"int salary = "<
}
{
friend Complex operator+(const Complex& x, const Complex& y);
friend Complex operator-(const Complex& x, const Complex& y);
friend Complex operator*(const Complex& x, const Complex& y);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Complex& c);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& i, const Complex& c);
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
Complex()
{
real = 0;
imag = 0;
}
Complex(double a, double b)
{
real = a;
imag = b;
}
~Complex(){}
double getReal() {return(real); }
double getImag() {return(imag); }
void print() {cout << real << " + " << imag << "i" << endl; }
};
Complex operator+(const Complex& x, const Complex& y)
{
Complex result;
result.real = x.real + y.real;
result.imag = x.imag + y.imag;
return result;
}
Complex operator-(const Complex& x, const Complex& y)
{
Complex result;
result.real = x.real - y.real;
result.imag = x.imag - y.imag;
return result;
}
Complex operator*(const Complex& x, const Complex& y)
{
Complex result;
result.real = x.real * y.real;
result.imag = x.imag * y.imag;
return result;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Complex& c)
{
os<< c.real << " + " << c.imag << "i" << endl;
return os;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, const Complex& c)
{
is>>(double)c.real>>(double)c.imag;
return is;
}
int main(void)
{
Complex x(2, 3), y(4, 6), z;
cout << "첫번째 복소수 x: ";
x.print();
cout << "두번째 복소수 y: ";
y.print();
z = x + y;
cout << "x + y = ";
z.print();
z = x - y;
cout << "x - y = ";
z.print();
z = x * y;
cout << "x * y = ";
z.print();
cout << "cout<
cout<
cin>>z;
cout<
}
9. [] 연산자도 중복이 가능하다.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class SymbolTable{
private:
string key[10];
int value[10];
int total;
public:
SymbolTable(){
for(int i=0; i< 10 ; i++){
key[i]="";
value[i] = 0;
total = 0;
}
}
void add(string key, int value)
{
for(int i=0; i< 10 ; i++){
if(this->value[i] == 0){
this->key[i] = key;
this->value[i] = value;
total++;
break;
}
}
}
void del(string key){
for(int i=0; i< 10; i++){
if( this->key[i] == key){
this->key[i]="";
this->value[i] = 0;
total--;
break;
}
}
}
int operator[](string key){
for(int i=0; i < 10; i++){
if( this->key[i] == key){
return this->value[i];
}
}
return -1;
}
};
int main()
{
SymbolTable table;
table.add("house", 100);
table.add("mouse", 200);
table.add("korea", 300);
table.del("mouse");
cout<< table["house"] << endl;
return 0;
}
10. 직원을 나타내는 Employee 클래스의 객체를 정수형으로 형변환하면 월급을 반환하도록 Employee 클래스 안에 형변환 함수를 중복 정의하라.
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Employee{
private:
string name;
int salary;
public:
Employee(){
name="Unknown";
salary = 0;
};
Employee(string name, int salary)
{
this->name = name;
this->salary = salary;
}
operator int() const
{
return salary;
}
void display()
{
cout<<"Name : "<
};
int main()
{
Employee e("홍길동", 100);
int salary = (int) e; // salary에 100이 저장된다
e.display();
cout<<"int salary = "<
}















































소개글