목차
1.서론
2. 실험방법
2.1 조성설계
2.2 상분석 및 미세구조 관찰
2.3 유전특성 측정
2.4 초전특성 측정
3. 결과 및 고찰
3.1 상분석 및 미세구조 관찰
3.2 유전특성
3.3 초전특성
4. 결론
2. 실험방법
2.1 조성설계
2.2 상분석 및 미세구조 관찰
2.3 유전특성 측정
2.4 초전특성 측정
3. 결과 및 고찰
3.1 상분석 및 미세구조 관찰
3.2 유전특성
3.3 초전특성
4. 결론
본문내용
e 온도는 PYS의 양이 0.01 mol% 증가함에 따라 10℃씩 감소하였다.
(3) 분극 조건은 능면정계에서는 80℃, 20㎸/㎝를 인가한 후 20분을 경과시키면 포화상태에 이르는 것으로 나타났으며, 정방정계의 경우에는 80℃, 50㎸/㎝ 이었다.
(4) 조립특성은 PYS가 0.05 mol% 첨가된 조성 중 RIST 5에서 상온 노이즈 및 상온 감도가 가장 우수한 것으로 판명되었다.
5. 참고문헌
(1) T. Kudo, T. Yazaki et al., J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 53, 6, 326 (1970)
(2) B. Jaffe, \"Piezoelectric ceramics\", p 115-134, Academic Press, (1971)
(3) 田中哲郞, 岡崎 淸 et al., 壓電 セラミツク材料, p 110-132, 학헌사, (1973)
(4) W. D. Kingery, H. K. Bowen, D. R. Uhlmann, \"Introduction to Ceramics\", p 58, John Wiley & Sons, (1976)
(5) Electronic Materials Manufacturers Asociation Standard, 6001-6006,
電子材料工業會, (1985)
(6) T. Ogawa, K. Wakino, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 24, Suppl. 24-3, 123 (1985)
(7) Takuro Ikeda, \"Fundamentals of piezoelectricity\", p 83-118, Oxford Univ.
Press, (1990)
(8) M. Yokosuka, T. Ochiai, M. Marutake, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 30(9B),
2228 (1991)
(9) Yuhuan Xu, \"Ferroelectric Materials and Their Applications\",
p 101-159, (1991)
(10) S. K. Wi, H. K. Kim, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 31(9A), 2825 (1992)
(11) K. Nagata, E. Harashima, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 33(9B), 5348 (1993)
(12) T. Kamiya, R. Mishima, T. Tsurumi et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys.,
32(9B) 4223 (1993)
비접촉식 IR 온도센서 개발
김선욱, 정회승, 황순철
Development of Non-contact IR Temperature Sensor
S.U.Kim, H.S.Jeong and S.C.Hwang
Abstract
Non-contact IR temperature sensor were prepared to set-up the system that can watch the temperature variation of BUS-BAR constantly. PZT-PYS ternary system was developed as the optimum composition of the piezoelectric material composing IR temperature sensor. Room temperature noise and sensitivity characteristics with 0.05mol% PYS were better than other cases. Specially, the composition of RIST 5 showed the best oven noise characteristics.
Key words : Non-contact IR temperature sensor, PZT-PYS ternary system, Poling condition, Oven noise
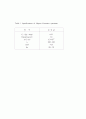
Table 1 Specifications of Nippon Ceramics specimen
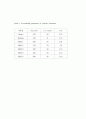
Table 2 Assembling properties of various specimen
Fig. 1 Block diagram of instrument for measuring
dielectric permittivity at various temperature
Fig. 2 Measurement system of output voltage
Fig. 3 Variation of lattice constant of xPYS-yPT-zPZ ceramics
for copmosition x=0.05
Fig. 4 SEM photographs of PYS-PZT ceramics
(a) PYS=0 (b) PYS=0.01mol (c) PYS=0.05mol
Fig. 5 Relative dielectric permittivity and tanδ of xPYS-yPT-zPZ
ceramics for various amounts of PYS
Fig. 6 Variation of curie temperature(Tc) of xPYS-yPT-zPZ ceramics
for various amounts of PYS
Fig. 7 Variation of coercive field(Ec) of xPYS-yPT-zPZ ceramics
for copmosition x=0.05
Fig. 8 Output voltage vs. frequency for 0.05PYS-0.38PT-0.57PZ ceramics
with various poling conditions
Fig. 9 Output voltage vs. frequency for 0.05PYS-0.74PT-0.21PZ ceramics
with various poling conditions
Fig. 10 Variation of output voltage of 0.05PYS-yPT-zPZ ceramics at 100㎐
with various poling conditions
Fig. 11 Output voltage vs. frequency for 0.05PYS-0.95PT ceramics
with various poling conditions
Fig. 12 Oven noise qualities of various specimen
(3) 분극 조건은 능면정계에서는 80℃, 20㎸/㎝를 인가한 후 20분을 경과시키면 포화상태에 이르는 것으로 나타났으며, 정방정계의 경우에는 80℃, 50㎸/㎝ 이었다.
(4) 조립특성은 PYS가 0.05 mol% 첨가된 조성 중 RIST 5에서 상온 노이즈 및 상온 감도가 가장 우수한 것으로 판명되었다.
5. 참고문헌
(1) T. Kudo, T. Yazaki et al., J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 53, 6, 326 (1970)
(2) B. Jaffe, \"Piezoelectric ceramics\", p 115-134, Academic Press, (1971)
(3) 田中哲郞, 岡崎 淸 et al., 壓電 セラミツク材料, p 110-132, 학헌사, (1973)
(4) W. D. Kingery, H. K. Bowen, D. R. Uhlmann, \"Introduction to Ceramics\", p 58, John Wiley & Sons, (1976)
(5) Electronic Materials Manufacturers Asociation Standard, 6001-6006,
電子材料工業會, (1985)
(6) T. Ogawa, K. Wakino, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 24, Suppl. 24-3, 123 (1985)
(7) Takuro Ikeda, \"Fundamentals of piezoelectricity\", p 83-118, Oxford Univ.
Press, (1990)
(8) M. Yokosuka, T. Ochiai, M. Marutake, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 30(9B),
2228 (1991)
(9) Yuhuan Xu, \"Ferroelectric Materials and Their Applications\",
p 101-159, (1991)
(10) S. K. Wi, H. K. Kim, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 31(9A), 2825 (1992)
(11) K. Nagata, E. Harashima, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 33(9B), 5348 (1993)
(12) T. Kamiya, R. Mishima, T. Tsurumi et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys.,
32(9B) 4223 (1993)
비접촉식 IR 온도센서 개발
김선욱, 정회승, 황순철
Development of Non-contact IR Temperature Sensor
S.U.Kim, H.S.Jeong and S.C.Hwang
Abstract
Non-contact IR temperature sensor were prepared to set-up the system that can watch the temperature variation of BUS-BAR constantly. PZT-PYS ternary system was developed as the optimum composition of the piezoelectric material composing IR temperature sensor. Room temperature noise and sensitivity characteristics with 0.05mol% PYS were better than other cases. Specially, the composition of RIST 5 showed the best oven noise characteristics.
Key words : Non-contact IR temperature sensor, PZT-PYS ternary system, Poling condition, Oven noise
Table 1 Specifications of Nippon Ceramics specimen
Table 2 Assembling properties of various specimen
Fig. 1 Block diagram of instrument for measuring
dielectric permittivity at various temperature
Fig. 2 Measurement system of output voltage
Fig. 3 Variation of lattice constant of xPYS-yPT-zPZ ceramics
for copmosition x=0.05
Fig. 4 SEM photographs of PYS-PZT ceramics
(a) PYS=0 (b) PYS=0.01mol (c) PYS=0.05mol
Fig. 5 Relative dielectric permittivity and tanδ of xPYS-yPT-zPZ
ceramics for various amounts of PYS
Fig. 6 Variation of curie temperature(Tc) of xPYS-yPT-zPZ ceramics
for various amounts of PYS
Fig. 7 Variation of coercive field(Ec) of xPYS-yPT-zPZ ceramics
for copmosition x=0.05
Fig. 8 Output voltage vs. frequency for 0.05PYS-0.38PT-0.57PZ ceramics
with various poling conditions
Fig. 9 Output voltage vs. frequency for 0.05PYS-0.74PT-0.21PZ ceramics
with various poling conditions
Fig. 10 Variation of output voltage of 0.05PYS-yPT-zPZ ceramics at 100㎐
with various poling conditions
Fig. 11 Output voltage vs. frequency for 0.05PYS-0.95PT ceramics
with various poling conditions
Fig. 12 Oven noise qualities of various specimen



































소개글