본문내용
alternativecomplement pathways
- IF ; C3, C1q, C4 in mesangium/ IgG, IgM in capillary loop
- EM ; subendothelial & mesangial electron-dense deposits
(2) Type II MPGN(dense deposit disease, not immune complexs)
- 10% of cases: children and young adults
- Marked thickening of GBM, but mesangial proliferation not
prominent so tram track not as apparent
- alternative complement pathway activation
→ decreased serum C3, but normal C1 and C4
→ decrease serum factor B and properdin
→ generation of C3NeF
- IF: C3 in mesangium in circular aggregates (mesangial rings)
IgG(-), C1q(-), C4(-)
- EM: lamina densa of GBM is transformed into irregular, ribbon-
like dense deposits
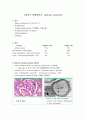
MPGN type 1
MPGN type 2
7. 임상상
(1) 단백뇨 (proteinuria)
(2) 저단백혈증 (hypoalbuminemia)
→ 소변을 통한 다량의 단백소실 및 이화작용 증가를 간에서의 알부민 합성이 따라가지 못함
(3) 부종
(4) 고지질혈증
→ 알부민 저하를 보상하기 위해 간에서는 알부민 합성이 증가하게 되는데 이때 지단백 합성도 함께 증가
→ TC, LDL, lipoprotein a level 의 상승
→ HDL 감소
(5) hypercoagulability
→ factor 9, 11, 12감소
→ factor 5, 8, 피브리노겐의 간합성증가
→ 혈소판수 및 응집능 증가
→ antithrombin 3의 감소
→ protein C/S level의 변화
(6) 합병증
- 감염: IgG 소실과 부종이 세균 배양액으로 작용하기 때문에
- 혈전생성 (renal vein thrombosis)
- 저혈압성 위기
→ 유효혈장량의 감소, 헤마토크릿과 맥박수 증가, 수분이 간질로 빠져나감
- 급성신부전
8. 치료
(1) 원인질환에 대한 치료
(2) 단백뇨 조절: ACE-I, ARB, NSAID, 단백질을 적당히 제한
→ 저알부민혈증 있다고 고단백식이 하면 안됨
(3) 합병증에 대한 치료
- 부종: 염분제한, 이뇨제 조심스럽게 사용
→ 이뇨제과다 사용은 prerenal azotemia유발, 1.0kg/day 이상의 수분 배출은 안됨. 폐부종, 고혈압의 위험이 있음
- 고지혈증: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
- 항응고 치료: 신부정맥혈전증이나 폐색전증시에.
- Ca, Vit D 보충
- 감염치료: 복막염의 위험 때문에
- IF ; C3, C1q, C4 in mesangium/ IgG, IgM in capillary loop
- EM ; subendothelial & mesangial electron-dense deposits
(2) Type II MPGN(dense deposit disease, not immune complexs)
- 10% of cases: children and young adults
- Marked thickening of GBM, but mesangial proliferation not
prominent so tram track not as apparent
- alternative complement pathway activation
→ decreased serum C3, but normal C1 and C4
→ decrease serum factor B and properdin
→ generation of C3NeF
- IF: C3 in mesangium in circular aggregates (mesangial rings)
IgG(-), C1q(-), C4(-)
- EM: lamina densa of GBM is transformed into irregular, ribbon-
like dense deposits
MPGN type 1
MPGN type 2
7. 임상상
(1) 단백뇨 (proteinuria)
(2) 저단백혈증 (hypoalbuminemia)
→ 소변을 통한 다량의 단백소실 및 이화작용 증가를 간에서의 알부민 합성이 따라가지 못함
(3) 부종
(4) 고지질혈증
→ 알부민 저하를 보상하기 위해 간에서는 알부민 합성이 증가하게 되는데 이때 지단백 합성도 함께 증가
→ TC, LDL, lipoprotein a level 의 상승
→ HDL 감소
(5) hypercoagulability
→ factor 9, 11, 12감소
→ factor 5, 8, 피브리노겐의 간합성증가
→ 혈소판수 및 응집능 증가
→ antithrombin 3의 감소
→ protein C/S level의 변화
(6) 합병증
- 감염: IgG 소실과 부종이 세균 배양액으로 작용하기 때문에
- 혈전생성 (renal vein thrombosis)
- 저혈압성 위기
→ 유효혈장량의 감소, 헤마토크릿과 맥박수 증가, 수분이 간질로 빠져나감
- 급성신부전
8. 치료
(1) 원인질환에 대한 치료
(2) 단백뇨 조절: ACE-I, ARB, NSAID, 단백질을 적당히 제한
→ 저알부민혈증 있다고 고단백식이 하면 안됨
(3) 합병증에 대한 치료
- 부종: 염분제한, 이뇨제 조심스럽게 사용
→ 이뇨제과다 사용은 prerenal azotemia유발, 1.0kg/day 이상의 수분 배출은 안됨. 폐부종, 고혈압의 위험이 있음
- 고지혈증: HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
- 항응고 치료: 신부정맥혈전증이나 폐색전증시에.
- Ca, Vit D 보충
- 감염치료: 복막염의 위험 때문에



























소개글