-
 1
1
-
 2
2
-
 3
3
-
 4
4
-
 5
5
-
 6
6
-
 7
7
-
 8
8
-
 9
9
-
 10
10
-
 11
11
-
 12
12
-
 13
13
-
 14
14
-
 15
15
-
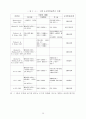 16
16
-
 17
17
-
 18
18
-
 19
19
-
 20
20
-
 21
21
-
 22
22
-
 23
23
-
 24
24
-
 25
25
-
 26
26
-
 27
27
-
 28
28
-
 29
29
-
 30
30
-
 31
31
-
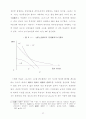 32
32
-
 33
33
-
 34
34
-
 35
35
-
 36
36
-
 37
37
-
 38
38
-
 39
39
-
 40
40
-
 41
41
-
 42
42
-
 43
43
-
 44
44
-
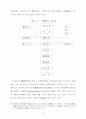 45
45
-
 46
46
-
 47
47
-
 48
48
-
 49
49
-
 50
50
-
 51
51
-
 52
52
-
 53
53
-
 54
54
-
 55
55
-
 56
56
-
 57
57
-
 58
58
-
 59
59
-
 60
60
-
 61
61
-
 62
62
-
 63
63
-
 64
64
-
 65
65
-
 66
66
-
 67
67
-
 68
68
-
 69
69
-
 70
70
-
 71
71
-
 72
72
-
 73
73
-
 74
74
-
 75
75
-
 76
76
-
 77
77
-
 78
78
-
 79
79
-
 80
80
-
 81
81
-
 82
82
-
 83
83
-
 84
84
-
 85
85
-
 86
86
-
 87
87
-
 88
88
-
 89
89
-
 90
90
-
 91
91
-
 92
92
-
 93
93
-
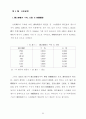 94
94
-
 95
95
-
 96
96
-
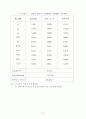 97
97
-
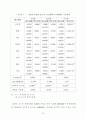 98
98
-
 99
99
-
 100
100
-
 101
101
-
 102
102
-
 103
103
-
 104
104
-
 105
105
-
 106
106
-
 107
107
-
 108
108
-
 109
109
-
 110
110
-
 111
111
-
 112
112
-
 113
113
-
 114
114
-
 115
115
-
 116
116
-
 117
117
-
 118
118
-
 119
119
-
 120
120
-
 121
121
-
 122
122
-
 123
123
-
 124
124
본 자료는 10페이지 의 미리보기를 제공합니다. 이미지를 클릭하여 주세요.

-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20
-
21
-
22
-
23
-
24
-
25
-
26
-
27
-
28
-
29
-
30
-
31
-
32
-
33
-
34
-
35
-
36
-
37
-
38
-
39
-
40
-
41
-
42
-
43
-
44
-
45
-
46
-
47
-
48
-
49
-
50
-
51
-
52
-
53
-
54
-
55
-
56
-
57
-
58
-
59
-
60
-
61
-
62
-
63
-
64
-
65
-
66
-
67
-
68
-
69
-
70
-
71
-
72
-
73
-
74
-
75
-
76
-
77
-
78
-
79
-
80
-
81
-
82
-
83
-
84
-
85
-
86
-
87
-
88
-
89
-
90
-
91
-
92
-
93
-
94
-
95
-
96
-
97
-
98
-
99
-
100
-
101
-
102
-
103
-
104
-
105
-
106
-
107
-
108
-
109
-
110
-
111
-
112
-
113
-
114
-
115
-
116
-
117
-
118
-
119
-
120
-
121
-
122
-
123
-
124


목차
제 Ⅰ 장 서 논
제 1 절 연구의 필요성
제 2 절 연구의 목적
제 3 절 연구의 방법 및 범위
제 4 절 선행연구의 검토
제 Ⅱ 장 농기계산업 수직적 통합의 이론적 배경과 부품거래 실태
제 1 절 수직적 통합의 이론적 배경
제 2 절 농기계산업의 특성과 거래비용이론의 적용성
제 3 절 농기계산업의 수직적 부품거래의 특성
제 Ⅲ 장 농기계산업의 수직적 통합의 결정요인분석
제 1 절 접근방법
제 2 절 실증분석모형
제 3 절 분석자료
제 4 절 분석결과
제 5 절 실제 거래방식과 예측된 거래방식간 비교
제 6 절 분석결과의 함의
제 Ⅳ 장 결 논
제 1 절 연구결과의 요약 및 시사점
제 2 절 연구의 한계 및 향후 과제
제 1 절 연구의 필요성
제 2 절 연구의 목적
제 3 절 연구의 방법 및 범위
제 4 절 선행연구의 검토
제 Ⅱ 장 농기계산업 수직적 통합의 이론적 배경과 부품거래 실태
제 1 절 수직적 통합의 이론적 배경
제 2 절 농기계산업의 특성과 거래비용이론의 적용성
제 3 절 농기계산업의 수직적 부품거래의 특성
제 Ⅲ 장 농기계산업의 수직적 통합의 결정요인분석
제 1 절 접근방법
제 2 절 실증분석모형
제 3 절 분석자료
제 4 절 분석결과
제 5 절 실제 거래방식과 예측된 거래방식간 비교
제 6 절 분석결과의 함의
제 Ⅳ 장 결 논
제 1 절 연구결과의 요약 및 시사점
제 2 절 연구의 한계 및 향후 과제
본문내용
riables as determinants of vertical integration: physical assets specificity, site specificity, human capital specificity, technology complexity, possibility of alternative supplier, component exchangeability, and labor intensity of the production process. Also, a dummy variable is included to control systematic differences among the three firms with regard to vertical integration.
For all the independent variables, managers made all responses on a five point Likert scale. Make-or-buy decisions were assigned a binary value with 0 for the decision to outsource, and 1 for the decision to vertically integrate. The data were analysed using the PROBIT estimation model of LIMDEP. The important results and implications of this study are illuminated below.
The coefficient on physical assets specificity is negative but insignificant. This suggests that if the physical assets are very specific then assemblers may rely on various forms of quasi-vertical integration to control the problems of opportunism and maladaptation. Also, to mitigate the problems of opportunism and maladaptation, agricultural machinery assemblers use \"credible commitments\" such as financial assistance, technological assistance, and managerial assistance. The coefficient of specific human capital is positive and significant. This suggests that assemblers search for another means to control the problems of opportunism in the case of specific human capital. As a result, assemblers would search for firm-specific skilled workers. The coefficient of technological complexity, a proxy variable for uncertainty, has a positive and slightly significant influence on vertical integration in the Korean agricultural machinery industry. The coefficient of site specificity is positive and significant. This implies that the components produced by assemblers are site specific components rather than outsourced components. The coefficient of alternative possibility of supplier and the coefficient of component exchangeability are both negative and significant. The coefficient of labor intensity of the production process is negative but insignificant. The coefficients of all dummy variables are negative and significant. However, the study could not determine clearly the different influence of vertical integration on each firm as this would require further delving into firm-specific attributes.
The model presented here which compared actual transaction patterns with predicted transaction patterns correctly predicted 338 of 369, or 91.6 percent, of the observations. Thus, the results ascertain that this analytical model makes a valuable contribution to Korean agricultural machinery assemblers\' decision on the choice of transaction pattern, that is, on the procurement of components in the industry.
Keywords : Korean Agricultural Machinery Industry, Transaction Cost Theory, Vertical Integration, Outsourcing, Agricultural Machinery Assembler, Agricultural Machinery Parts Supplier
Student Number : 90507-803
For all the independent variables, managers made all responses on a five point Likert scale. Make-or-buy decisions were assigned a binary value with 0 for the decision to outsource, and 1 for the decision to vertically integrate. The data were analysed using the PROBIT estimation model of LIMDEP. The important results and implications of this study are illuminated below.
The coefficient on physical assets specificity is negative but insignificant. This suggests that if the physical assets are very specific then assemblers may rely on various forms of quasi-vertical integration to control the problems of opportunism and maladaptation. Also, to mitigate the problems of opportunism and maladaptation, agricultural machinery assemblers use \"credible commitments\" such as financial assistance, technological assistance, and managerial assistance. The coefficient of specific human capital is positive and significant. This suggests that assemblers search for another means to control the problems of opportunism in the case of specific human capital. As a result, assemblers would search for firm-specific skilled workers. The coefficient of technological complexity, a proxy variable for uncertainty, has a positive and slightly significant influence on vertical integration in the Korean agricultural machinery industry. The coefficient of site specificity is positive and significant. This implies that the components produced by assemblers are site specific components rather than outsourced components. The coefficient of alternative possibility of supplier and the coefficient of component exchangeability are both negative and significant. The coefficient of labor intensity of the production process is negative but insignificant. The coefficients of all dummy variables are negative and significant. However, the study could not determine clearly the different influence of vertical integration on each firm as this would require further delving into firm-specific attributes.
The model presented here which compared actual transaction patterns with predicted transaction patterns correctly predicted 338 of 369, or 91.6 percent, of the observations. Thus, the results ascertain that this analytical model makes a valuable contribution to Korean agricultural machinery assemblers\' decision on the choice of transaction pattern, that is, on the procurement of components in the industry.
Keywords : Korean Agricultural Machinery Industry, Transaction Cost Theory, Vertical Integration, Outsourcing, Agricultural Machinery Assembler, Agricultural Machinery Parts Supplier
Student Number : 90507-803
추천자료
 [카지노][카지노산업]카지노(카지노산업)의 역사, 카지노(카지노산업)의 특성, 카지노(카지노...
[카지노][카지노산업]카지노(카지노산업)의 역사, 카지노(카지노산업)의 특성, 카지노(카지노... [서비스][서비스산업][서비스업][서비스업과 고객간 관계][기업][서비스산업의 동향]서비스의...
[서비스][서비스산업][서비스업][서비스업과 고객간 관계][기업][서비스산업의 동향]서비스의... [공정경쟁][방송산업][방송환경][방송]DMB산업과 공정경쟁, 유료방송산업과 공정경쟁, 지상파...
[공정경쟁][방송산업][방송환경][방송]DMB산업과 공정경쟁, 유료방송산업과 공정경쟁, 지상파... [방송산업]방송산업 공정경쟁의 중요성과 방송산업 공정경쟁의 현황, 방송산업 공정경쟁의 문...
[방송산업]방송산업 공정경쟁의 중요성과 방송산업 공정경쟁의 현황, 방송산업 공정경쟁의 문... [ASP][ASP산업][ASP산업 구분][ASP산업 현황][ASP산업 사례][데이콤][ASP산업 시장 전망]ASP...
[ASP][ASP산업][ASP산업 구분][ASP산업 현황][ASP산업 사례][데이콤][ASP산업 시장 전망]ASP... [금융겸업, 금융산업조직론, 겸업은행, 금융제도, 인터넷뱅킹, 금융, 금융산업, 금융겸업화, ...
[금융겸업, 금융산업조직론, 겸업은행, 금융제도, 인터넷뱅킹, 금융, 금융산업, 금융겸업화, ... [산업기술정책, 산업기술정책 기본방향, 산업기술정책 추진계획, 지역화]산업기술정책의 기본...
[산업기술정책, 산업기술정책 기본방향, 산업기술정책 추진계획, 지역화]산업기술정책의 기본... [한일자동차산업, 숙련형성시스템, 혁신네트워크, 노동자숙련, 기업간연계]한일자동차산업의 ...
[한일자동차산업, 숙련형성시스템, 혁신네트워크, 노동자숙련, 기업간연계]한일자동차산업의 ... [벤처기업 산업재산권][벤처기업][벤처][산업재산권][벤처기업 산업재산권 개념]벤처기업 산...
[벤처기업 산업재산권][벤처기업][벤처][산업재산권][벤처기업 산업재산권 개념]벤처기업 산... 인도의 ICT 산업 동향과 시사점 (인도의 산업구조, 인도 ICT 산업의 현황, 인도 기업의 그린 ...
인도의 ICT 산업 동향과 시사점 (인도의 산업구조, 인도 ICT 산업의 현황, 인도 기업의 그린 ... [산업보안학 産業保安學] 한국의 산업보안정책과 제도 - 산업기술보호 기본계획과 시행계획 ...
[산업보안학 産業保安學] 한국의 산업보안정책과 제도 - 산업기술보호 기본계획과 시행계획 ... [산업보안학 産業保安學] 외국의 산업보안정책(industrial security policy) - 미국의 산업보...
[산업보안학 産業保安學] 외국의 산업보안정책(industrial security policy) - 미국의 산업보... [서비스업][서비스산업][서비스]서비스업(서비스산업)의 특징, 서비스업(서비스산업)의 규제,...
[서비스업][서비스산업][서비스]서비스업(서비스산업)의 특징, 서비스업(서비스산업)의 규제,... [외식산업의 특징] 외식산업의 특성 - 외식산업의 산업적인 특성 및 사업적인 특성, 외식산업...
[외식산업의 특징] 외식산업의 특성 - 외식산업의 산업적인 특성 및 사업적인 특성, 외식산업...


















소개글