
-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20
-
21
-
22
-
23
-
24
-
25
-
26
-
27
-
28
-
29
-
30
-
31
-
32
-
33
-
34
-
35
-
36
-
37
-
38
-
39
-
40
-
41
-
42
-
43
-
44
-
45
-
46
-
47
-
48
-
49
-
50
-
51
-
52
-
53
-
54
-
55
-
56
-
57
-
58
-
59
-
60
-
61
-
62
-
63
-
64
-
65
-
66
-
67
-
68
-
69
-
70


본문내용
Radiologic Findings of
Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia
ATS/ERS Consensus
International standard
: Diagnostic criteria & terminology
7 clinico-radiologic-pathologic entities
Term of “pattern”
: Histopathologic diagnosis
Roles of HRCT
Separate pts with typical IPF/UIP
Detecting clues to non-IIP dz
Selecting appropriate site for biopsy
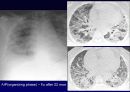
Follow-up
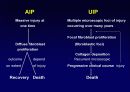
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Introduction
Chronic fibrosing interstitial pneumonia
Histologic pattern of UIP
Exclusion of other known causes of ILD
Clinical Features
Age of onset > usually 50 yrs
Gradual symptom of dyspnea
PFT : restrictive, DLCo↓
Median survival : 2.5-3.5 yrs
BALF : total cell count, neutrophils↑
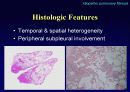
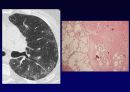
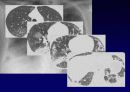
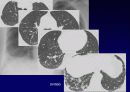
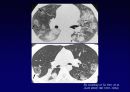
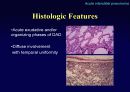
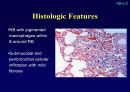
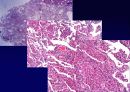
Histologic Features
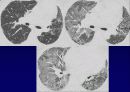
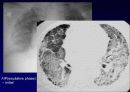
Temporal & spatial heterogeneity
Peripheral subpleural involvement
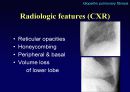
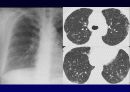
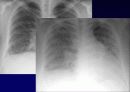
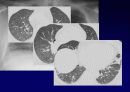
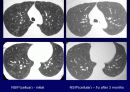
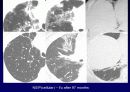
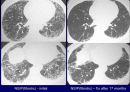
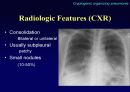
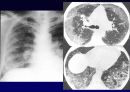
Radiologic features (CXR)
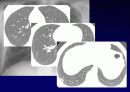
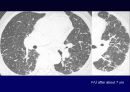
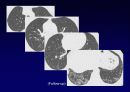
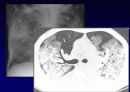
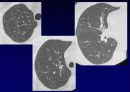
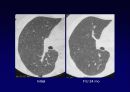
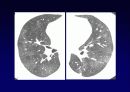
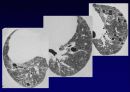
Reticular opacities
Honeycombing
Peripheral & basal
Volume loss
ATS/ERS Consensus
International standard
: Diagnostic criteria & terminology
7 clinico-radiologic-pathologic entities
Term of “pattern”
: Histopathologic diagnosis
Roles of HRCT
Separate pts with typical IPF/UIP
Detecting clues to non-IIP dz
Selecting appropriate site for biopsy
Follow-up
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Introduction
Chronic fibrosing interstitial pneumonia
Histologic pattern of UIP
Exclusion of other known causes of ILD
Clinical Features
Age of onset > usually 50 yrs
Gradual symptom of dyspnea
PFT : restrictive, DLCo↓
Median survival : 2.5-3.5 yrs
BALF : total cell count, neutrophils↑
Histologic Features
Temporal & spatial heterogeneity
Peripheral subpleural involvement
Radiologic features (CXR)
Reticular opacities
Honeycombing
Peripheral & basal
Volume loss


























































소개글