-
1
-
2
-
3
-
4
-
5
-
6
-
7
-
8
-
9
-
10
-
11
-
12
-
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
-
17
-
18
-
19
-
20
-
21
-
22
-
23
-
24
-
25
-
26
-
27
-
28
-
29
-
30
-
31
-
32
-
33
-
34
-
35
-
36
-
37
-
38
-
39
-
40
-
41
-
42
-
43
-
44
-
45
-
46
-
47
-
48
-
49
-
50
-
51
-
52
-
53
-
54
-
55
-
56
-
57
-
58
-
59
-
60
-
61
-
62
-
63
-
64
-
65
-
66
-
67
-
68
-
69
-
70
-
71
-
72
-
73
-
74
-
75
-
76
-
77
-
78
-
79
-
80
-
81
-
82
-
83
-
84
-
85
-
86
-
87
-
88
-
89
-
90
-
91
-
92
-
93
-
94
-
95
-
96
-
97
-
98
-
99
-
100


목차
중증도 측정도구를 이용한 관상동맥우회로조성술의 보정사망률에 관한 연구
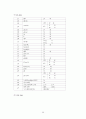
<제목차례>
제1장 연구의 배경 및 필요성
제2장 이론적 고찰
1. 의료의 질 평가도구로서 사망률 지표의 타당성
2. 결과 측정의 위험요인 보정
2.1 위험요인 보정의 필요성
2.2 위험요인의 선정
3. 중증도 측정 도구(severity measuring tools
4. 위험요인 보정 CABG 사망률에 관한 연구
제3장 연구 목적
제4장 연구 자료 및 방법
1. 연구 자료
1.1 조사 대상
1.2 자료 수집
1.3 자료 처리
1.4 조사 도구
1) MedisGroups
2) Computerized Severity Index
3) Disease Staging
4) APACHEⅢ
5) KDRG
6) 조사양식
2. 연구 방법
2.1 단순사망률의 산출
2.2 중증도 점수 산출
2.3 사망률 예측 모형의 구축과 중증도 보정사망률의 산출
2.4 예측 모형의 통계적 적합성 평가
2.5 병원별 성과 비교
1) 예측사망률의 신뢰구간과 측정사망률의 비교
2) 예측사망자수와 관찰사망자수 비(mortality performance index) 산출
3) z score 산출
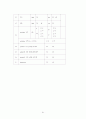
제5장 연구 결과
1. 조사 대상 병원 및 환자의 특성
1.1 조사 대상 병원의 특성
1) 인구학적 특성
2. 단순사망률
3. 중증도 측정 결과
3.1 전체 대상자의 중증도
3.2 병원별 중증도
1) MedisGroups
(2) CSI
(3) DS
(4) APACHEⅢ
3.3 중증도 점수대별 단순사망률
4. 중증도 보정모형의 통계적 적합성
5. 중증도 보정사망률
6. 병원간 성과 비교
6.1 측정사망률과 예측사망률 신뢰구간의 비교
1) MedisGroups
2) CSI
3) DS
4) APACHEⅢ
5) KDRG
6.2 관찰사망자수와 예측사망자수의 비(Mortality Performance Index)
6.3 z score
제6장
1. 연구 자료 및 방법에 대한 고찰
2. 연구 결과에 대한 고찰
3. 정책 대안
제7장 결론
참고 문헌
부록 1. 중증도 도구별 점수 산출 방법
부록 2. 의무기록 조사양식지 및 조사지침
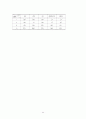
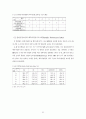
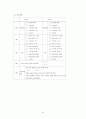
<표차례>
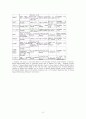
표 2-1. 위험요인목
표 2-2. 중증도 측정 도구의 비교
표 2-3. CABG 수술 사망의 유의한 위험요인
표 4-1. MedisGroups empirical version의 조사항목
표 4-2. CSI의 조사 항목
표 4-3. Disease Staging for coronary artery disease의 조사 항목
표 4-4. APACHEⅢ의 조사 항목
표 5-1. 대상 병원의 지역 및 병원 구분 비교
표 5-2. 조사대상자의 인구학적 특성
표 5-3. 병원별 조사대상자의 연령 및 성별 분포 비교
표 5-4. 수술 우선 순위 구분
표 5-6. 병원별 단순사망률
표 5-7. 성별 단순사망률
표 5-8. 연령대별 단순사망률
표 5-9. 측정 도구별 중증도 점수의 분포
표 5-10. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(MG)
표 5-11. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(CSI)
표 5-12. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(DS)
표 5-13. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(APACHEⅢ)
표 5-14. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(KDRG)
표 5-15. 중증도 점수대별 단순사망률
표 5-16. 위험요인 보정모형의 적합성 비교
표 5-17. 도구별 예측 사망률의 최상 및 최하 10분위의 측정사망률 비교
표 5-18. 중증도 측정 도구별 병원별 보정사망률
표 5-19. 병원별 측정사망률과 예측사망률 신뢰구간 비교의 종합
표 5-20. 병원별 Mortality Performance Index 비교
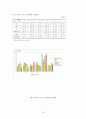
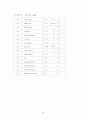
<그림차례>
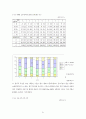
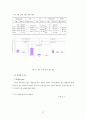
그림 5-1 병원별 연령 구성 비교
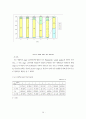
그림 5-3 측정 도구별 중증도 점수 분포
그림 5-5 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(CSI)
그림 5-6 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(DS)
그림 5-7 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(APACHEⅢ)
그림 5-8 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(KDRG)
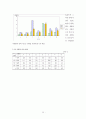
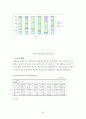
그림 5-9 중증도 측정 도구별 병원별 보정사망률
그림 5-10 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(MG)
그림 5-11 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(CSI)
그림 5-12 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(DS)
그림 5-13 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(APACHEⅢ)
그림 5-14 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(KDRG)
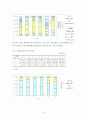
그림 5-15 병원별 도구별 MPI 비교
<제목차례>
제1장 연구의 배경 및 필요성
제2장 이론적 고찰
1. 의료의 질 평가도구로서 사망률 지표의 타당성
2. 결과 측정의 위험요인 보정
2.1 위험요인 보정의 필요성
2.2 위험요인의 선정
3. 중증도 측정 도구(severity measuring tools
4. 위험요인 보정 CABG 사망률에 관한 연구
제3장 연구 목적
제4장 연구 자료 및 방법
1. 연구 자료
1.1 조사 대상
1.2 자료 수집
1.3 자료 처리
1.4 조사 도구
1) MedisGroups
2) Computerized Severity Index
3) Disease Staging
4) APACHEⅢ
5) KDRG
6) 조사양식
2. 연구 방법
2.1 단순사망률의 산출
2.2 중증도 점수 산출
2.3 사망률 예측 모형의 구축과 중증도 보정사망률의 산출
2.4 예측 모형의 통계적 적합성 평가
2.5 병원별 성과 비교
1) 예측사망률의 신뢰구간과 측정사망률의 비교
2) 예측사망자수와 관찰사망자수 비(mortality performance index) 산출
3) z score 산출
제5장 연구 결과
1. 조사 대상 병원 및 환자의 특성
1.1 조사 대상 병원의 특성
1) 인구학적 특성
2. 단순사망률
3. 중증도 측정 결과
3.1 전체 대상자의 중증도
3.2 병원별 중증도
1) MedisGroups
(2) CSI
(3) DS
(4) APACHEⅢ
3.3 중증도 점수대별 단순사망률
4. 중증도 보정모형의 통계적 적합성
5. 중증도 보정사망률
6. 병원간 성과 비교
6.1 측정사망률과 예측사망률 신뢰구간의 비교
1) MedisGroups
2) CSI
3) DS
4) APACHEⅢ
5) KDRG
6.2 관찰사망자수와 예측사망자수의 비(Mortality Performance Index)
6.3 z score
제6장
1. 연구 자료 및 방법에 대한 고찰
2. 연구 결과에 대한 고찰
3. 정책 대안
제7장 결론
참고 문헌
부록 1. 중증도 도구별 점수 산출 방법
부록 2. 의무기록 조사양식지 및 조사지침
<표차례>
표 2-1. 위험요인목
표 2-2. 중증도 측정 도구의 비교
표 2-3. CABG 수술 사망의 유의한 위험요인
표 4-1. MedisGroups empirical version의 조사항목
표 4-2. CSI의 조사 항목
표 4-3. Disease Staging for coronary artery disease의 조사 항목
표 4-4. APACHEⅢ의 조사 항목
표 5-1. 대상 병원의 지역 및 병원 구분 비교
표 5-2. 조사대상자의 인구학적 특성
표 5-3. 병원별 조사대상자의 연령 및 성별 분포 비교
표 5-4. 수술 우선 순위 구분
표 5-6. 병원별 단순사망률
표 5-7. 성별 단순사망률
표 5-8. 연령대별 단순사망률
표 5-9. 측정 도구별 중증도 점수의 분포
표 5-10. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(MG)
표 5-11. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(CSI)
표 5-12. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(DS)
표 5-13. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(APACHEⅢ)
표 5-14. 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(KDRG)
표 5-15. 중증도 점수대별 단순사망률
표 5-16. 위험요인 보정모형의 적합성 비교
표 5-17. 도구별 예측 사망률의 최상 및 최하 10분위의 측정사망률 비교
표 5-18. 중증도 측정 도구별 병원별 보정사망률
표 5-19. 병원별 측정사망률과 예측사망률 신뢰구간 비교의 종합
표 5-20. 병원별 Mortality Performance Index 비교
<그림차례>
그림 5-1 병원별 연령 구성 비교
그림 5-3 측정 도구별 중증도 점수 분포
그림 5-5 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(CSI)
그림 5-6 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(DS)
그림 5-7 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(APACHEⅢ)
그림 5-8 병원별 중증도 점수 분포(KDRG)
그림 5-9 중증도 측정 도구별 병원별 보정사망률
그림 5-10 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(MG)
그림 5-11 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(CSI)
그림 5-12 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(DS)
그림 5-13 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(APACHEⅢ)
그림 5-14 병원별 예측사망률과 측정사망률(KDRG)
그림 5-15 병원별 도구별 MPI 비교
본문내용
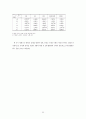
으로 간주함.
(2) chest X-ray 항목은 방사선 의사의 판독 내용을 위주로 해서 주치의의 progress note를 참조
(3) ischemic cerebral infarction은 brain CT 판독 내용을 참조하여 기록
Severity-Adjusted Mortality Rates of
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery in Korea
Young-Dae Kwon
Department of Health Policy and Management
College of Medicine
Seoul National University
(Directed by Professor Youngsoo Shin)
Background
Since the implementation of 'Hospital Service Evaluation Program' in 1995, most of hospitals and medical professionals have been interested in assessment and improvement of quality in health care. Among 'structure', 'process' and 'outcome' approaches, outcome evaluation is considered as the most direct and best approach to assess the quality of health care providers. Risk-adjustment is an essential method to compare outcome across providers.
Objectives
This study has aims to judge performance of hospitals by severity adjusted mortality rates of coronary artery bypass graft(CABG) surgery in Korea and to develop policies for use severity adjusted mortality as an effective indicator for hospital performance.
Methods
1) subject
Medical records of 584 patients who got the CABG operation in 6 general hospitals during 1996 and 1997 were reviewed by trained nurses.
2) severity measuring tools
Five measuring tools including MedisGroups, Disease Staging(DS), Computerized Severity Index(CSI), APACHEⅢ, and KDRG were used to quantify severity of patients.
3) severity adjustment
Using each severity method, a predictive probability of death was calculated for each patient in the sample from a multivariate logistic regression model including the severity score, age ,and sex. The statistical performance of each severity method model was evaluated by using c-statistic and R2.
4) evaluation of hospital performance
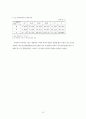
For each severity method, we calculated ratio of observed number to expected number of deaths and z score((observed number of deaths - expected number of deaths)/square root of the variance in the number of deaths), and compared observed mortality rate with confidence interval of expected mortality rate for each hospital.
Results and Discussions
The overall in-hospital mortality was 7.0%, ranged from 2.7% to 15.7% by hospital. The range of mortality rate was decreased after severity adjustment. The five severity systems varied in their statistical performance for predicting deaths at the individual patient level. All models had higher c-statistic and R2 values than the model containing only age and sex. In relative hospital performance evaluation, all methods showed the same result in assigning outlier.
We concluded that severity-adjusted mortality rate of CABG surgery might be applied as an indicator for hospital performance evaluation in Korea. But more pilot studies and improvement of methodologies has to be done to use it as quality indicator.
Key words: severity adjustment, mortality rate, coronary artery bypass graft surgery, quality assessment, hospital performance
(2) chest X-ray 항목은 방사선 의사의 판독 내용을 위주로 해서 주치의의 progress note를 참조
(3) ischemic cerebral infarction은 brain CT 판독 내용을 참조하여 기록
Severity-Adjusted Mortality Rates of
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery in Korea
Young-Dae Kwon
Department of Health Policy and Management
College of Medicine
Seoul National University
(Directed by Professor Youngsoo Shin)
Background
Since the implementation of 'Hospital Service Evaluation Program' in 1995, most of hospitals and medical professionals have been interested in assessment and improvement of quality in health care. Among 'structure', 'process' and 'outcome' approaches, outcome evaluation is considered as the most direct and best approach to assess the quality of health care providers. Risk-adjustment is an essential method to compare outcome across providers.
Objectives
This study has aims to judge performance of hospitals by severity adjusted mortality rates of coronary artery bypass graft(CABG) surgery in Korea and to develop policies for use severity adjusted mortality as an effective indicator for hospital performance.
Methods
1) subject
Medical records of 584 patients who got the CABG operation in 6 general hospitals during 1996 and 1997 were reviewed by trained nurses.
2) severity measuring tools
Five measuring tools including MedisGroups, Disease Staging(DS), Computerized Severity Index(CSI), APACHEⅢ, and KDRG were used to quantify severity of patients.
3) severity adjustment
Using each severity method, a predictive probability of death was calculated for each patient in the sample from a multivariate logistic regression model including the severity score, age ,and sex. The statistical performance of each severity method model was evaluated by using c-statistic and R2.
4) evaluation of hospital performance
For each severity method, we calculated ratio of observed number to expected number of deaths and z score((observed number of deaths - expected number of deaths)/square root of the variance in the number of deaths), and compared observed mortality rate with confidence interval of expected mortality rate for each hospital.
Results and Discussions
The overall in-hospital mortality was 7.0%, ranged from 2.7% to 15.7% by hospital. The range of mortality rate was decreased after severity adjustment. The five severity systems varied in their statistical performance for predicting deaths at the individual patient level. All models had higher c-statistic and R2 values than the model containing only age and sex. In relative hospital performance evaluation, all methods showed the same result in assigning outlier.
We concluded that severity-adjusted mortality rate of CABG surgery might be applied as an indicator for hospital performance evaluation in Korea. But more pilot studies and improvement of methodologies has to be done to use it as quality indicator.
Key words: severity adjustment, mortality rate, coronary artery bypass graft surgery, quality assessment, hospital performance