목차
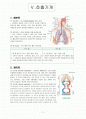
Ⅴ. 호흡기계
1. 해부학
(1) 상부기도
(2) 하부기도
(3) 폐
2. 생리학
(1) 외호흡 external respiration
(2) 내호흡 internal respiration
obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD)Ⅵ. 만성 폐쇄성 폐질환
(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD)
1. 정의
2. 종류
1) 폐기종(emphysema)
2) 만성 기관지염(chronic bronchitis)
3) 기관지 천식(bronchial asthma)
4) 기관지 확장증(bronchiectasis)
3. 발병기전(Pathogenesis)
4. 검사
1) 방사선 검사
2) ABGA (Arterial Blood Gas Analysis)
3) PFT (Pulmonary Function Test)
4) 기관지경 검사(Bronchoscopy)
5) 객담검사
5. 진단
1) 임상증상
2) 신체검사
3) 검사실 성적
4) 만성폐쇄성폐질환의 중증도
6. 치료
1) 목표
2) 기본 방침
1. 해부학
(1) 상부기도
(2) 하부기도
(3) 폐
2. 생리학
(1) 외호흡 external respiration
(2) 내호흡 internal respiration
obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD)Ⅵ. 만성 폐쇄성 폐질환
(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, COPD)
1. 정의
2. 종류
1) 폐기종(emphysema)
2) 만성 기관지염(chronic bronchitis)
3) 기관지 천식(bronchial asthma)
4) 기관지 확장증(bronchiectasis)
3. 발병기전(Pathogenesis)
4. 검사
1) 방사선 검사
2) ABGA (Arterial Blood Gas Analysis)
3) PFT (Pulmonary Function Test)
4) 기관지경 검사(Bronchoscopy)
5) 객담검사
5. 진단
1) 임상증상
2) 신체검사
3) 검사실 성적
4) 만성폐쇄성폐질환의 중증도
6. 치료
1) 목표
2) 기본 방침
본문내용
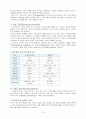
소비 증가
단독제제
MDI(㎍)
Nebulizer(㎎)
Oral(㎎)
Duration of action
Fenoterol
100-200
0.5-2.0
4-6
Salbutamol
100-200
2.5-5.0
4
4-6
Terbutaline
250-500
5-10
5
4-
Formoterol
12-24
12+
Salmeterol
50-100
12+
Bambuterol
10
Procaterol
병용제제
Fenoterol/Ipratropium
Salbutamol/Ipratropium
베타 2 항진제 제형
다. methylxanthine
기전 : 비특이적인 PDE 억제제, adenosine 수용체 길항제(antagonist)
기도염증을 감소시키는 항염증효과
기관지확장제 흡입치료에 대한 반응이 만족스럽지 못한 경우에 추가하여 사용
저녁에 투여하면 야간에 FEV1 감소와 아침의 호흡기 증상을 경감시킴.
Collateral ventilation, respiratory muscle function, mucocilary clearance and central respiratory drive를 증가시킨다.
기관지확장 효과는 약하며 therapeutic and toxic ranges 사이의 margine이 좁아서 치료 효과는 5㎍/㎖ 이상에서 나타나며 15㎍/㎖ 이상에서 부작용이 현저하게 증가하므로 혈중농도를 정기적으로 측정하여 8-12㎍/㎖로 유지하는 것이 안전하다.
dose로 투여하고 유지 용량은 0.4㎎/㎏/hour을 기준으로 한다.
환자에 따른 용량 변화 : 흡연자는 50% 정도까지 증량
liver insufficiency or hypoxemic patient는 25-50% 감량
심부전 환자는 50% 감량
다른 약물과의 상호작용을 고려하여야 한다.
부작용 :
소화기 : 오심과 구토, 심와부 통증, 설사, 혈변
신경계 : 대발작(grand mal seizure) 유발
두통, 불면증, irritabilitry, restlessness, muscle twitching
순환기 : 저혈압, 심계항진, artrial & ventricular arrhythmia 유발
호흡기 : 과호흡
신장 : diuresis, 알부민뇨
기타 : 고혈당, SIADH
지속성 경구제
Aminophylline(SR) 225㎎ Theophylline(SR) 100, 130, 200, 260㎎
③ 항염증제(Antiinflammatory agents)
가. Glucocorticosteroids
prolonged treatment with inhaled glucocorticosteroids does not modify the long-term decline in FEV1 in COPD
삶의 질을 향상시키고 악화 횟수를 감소시킨다.
적응증 : COPD with a documented spirometric response to inhaled steroids
FEV1 < 50% predicted인 환자 중에서 악화가 반복되는 환자
Therapeutic trial
trial of 6 weeks to 3 months with inhaled glucocorticosteroids
long-term treatment with oral glucocorticosteroids is not recommended
부작용 : 당뇨병, 골다공증, 백내장
Glucocorticosteroid 제형
- 경구제
Methylprednisolone, Prednisolone, Prednisone
- 흡입제
Beclomethasone dipropionate 42 & 84 mcg/puff
Budesonide turbuhaler 200 mcg/puff
Fluticasone MDI, disket 100, 250, 500 mcg/puff
Flunisolide 250 mcg/puff
Triamcinolone acetonide 100 mcg/puff
- 베타항진제와 병용제제
Salmeterol/Fluticasone
Formoterol/Budesonide
나. phosphodiesterase inhibitor
PDE4 inhibitor
(3) 이차적 내과 합병증 치료(Correcting secondary physiologic alterations)
① Prevention and early treatment of recurrent or chronic infection
가. Antibiotics
나. vaccines
② Hypoxemia
가. Oxygen therapy
나. Method of therapy
③ Pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale
④ Hypercarnia
(4) 호흡기 증상의 감소 및 삶의 질 향상(Optimizing functional capability)
목표 : reduce respiratory symptoms, anxiety, depression
reduce the need for medical and hospital care
improve exercise performance and the guality of life
① 재활치료
Exercise conditioning
Upper extremity training
Respiratory muscle training
Respiratory muscle rest
② 영양요법
Undernutrition in 25% of COPD and up to 50% of hospitalized patients
associated with reduced respiratory muscle function and increased mortality
BMI가 18 이하인 경우에 영양요법 실시
③ Dyspnea의 치료
④ Physical and occupational therapy
⑤ Psychosocial rehabilitation
(5) 기타 치료(Other issues in treatment)
① α1-antitrypsin augmentation
② 수술요법
bullectomy
volume reduction surgery
lung transplantation
단독제제
MDI(㎍)
Nebulizer(㎎)
Oral(㎎)
Duration of action
Fenoterol
100-200
0.5-2.0
4-6
Salbutamol
100-200
2.5-5.0
4
4-6
Terbutaline
250-500
5-10
5
4-
Formoterol
12-24
12+
Salmeterol
50-100
12+
Bambuterol
10
Procaterol
병용제제
Fenoterol/Ipratropium
Salbutamol/Ipratropium
베타 2 항진제 제형
다. methylxanthine
기전 : 비특이적인 PDE 억제제, adenosine 수용체 길항제(antagonist)
기도염증을 감소시키는 항염증효과
기관지확장제 흡입치료에 대한 반응이 만족스럽지 못한 경우에 추가하여 사용
저녁에 투여하면 야간에 FEV1 감소와 아침의 호흡기 증상을 경감시킴.
Collateral ventilation, respiratory muscle function, mucocilary clearance and central respiratory drive를 증가시킨다.
기관지확장 효과는 약하며 therapeutic and toxic ranges 사이의 margine이 좁아서 치료 효과는 5㎍/㎖ 이상에서 나타나며 15㎍/㎖ 이상에서 부작용이 현저하게 증가하므로 혈중농도를 정기적으로 측정하여 8-12㎍/㎖로 유지하는 것이 안전하다.
dose로 투여하고 유지 용량은 0.4㎎/㎏/hour을 기준으로 한다.
환자에 따른 용량 변화 : 흡연자는 50% 정도까지 증량
liver insufficiency or hypoxemic patient는 25-50% 감량
심부전 환자는 50% 감량
다른 약물과의 상호작용을 고려하여야 한다.
부작용 :
소화기 : 오심과 구토, 심와부 통증, 설사, 혈변
신경계 : 대발작(grand mal seizure) 유발
두통, 불면증, irritabilitry, restlessness, muscle twitching
순환기 : 저혈압, 심계항진, artrial & ventricular arrhythmia 유발
호흡기 : 과호흡
신장 : diuresis, 알부민뇨
기타 : 고혈당, SIADH
지속성 경구제
Aminophylline(SR) 225㎎ Theophylline(SR) 100, 130, 200, 260㎎
③ 항염증제(Antiinflammatory agents)
가. Glucocorticosteroids
prolonged treatment with inhaled glucocorticosteroids does not modify the long-term decline in FEV1 in COPD
삶의 질을 향상시키고 악화 횟수를 감소시킨다.
적응증 : COPD with a documented spirometric response to inhaled steroids
FEV1 < 50% predicted인 환자 중에서 악화가 반복되는 환자
Therapeutic trial
trial of 6 weeks to 3 months with inhaled glucocorticosteroids
long-term treatment with oral glucocorticosteroids is not recommended
부작용 : 당뇨병, 골다공증, 백내장
Glucocorticosteroid 제형
- 경구제
Methylprednisolone, Prednisolone, Prednisone
- 흡입제
Beclomethasone dipropionate 42 & 84 mcg/puff
Budesonide turbuhaler 200 mcg/puff
Fluticasone MDI, disket 100, 250, 500 mcg/puff
Flunisolide 250 mcg/puff
Triamcinolone acetonide 100 mcg/puff
- 베타항진제와 병용제제
Salmeterol/Fluticasone
Formoterol/Budesonide
나. phosphodiesterase inhibitor
PDE4 inhibitor
(3) 이차적 내과 합병증 치료(Correcting secondary physiologic alterations)
① Prevention and early treatment of recurrent or chronic infection
가. Antibiotics
나. vaccines
② Hypoxemia
가. Oxygen therapy
나. Method of therapy
③ Pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale
④ Hypercarnia
(4) 호흡기 증상의 감소 및 삶의 질 향상(Optimizing functional capability)
목표 : reduce respiratory symptoms, anxiety, depression
reduce the need for medical and hospital care
improve exercise performance and the guality of life
① 재활치료
Exercise conditioning
Upper extremity training
Respiratory muscle training
Respiratory muscle rest
② 영양요법
Undernutrition in 25% of COPD and up to 50% of hospitalized patients
associated with reduced respiratory muscle function and increased mortality
BMI가 18 이하인 경우에 영양요법 실시
③ Dyspnea의 치료
④ Physical and occupational therapy
⑤ Psychosocial rehabilitation
(5) 기타 치료(Other issues in treatment)
① α1-antitrypsin augmentation
② 수술요법
bullectomy
volume reduction surgery
lung transplantation
추천자료
 Oleic acid로 유발한 가토의 호흡부전증에서 통상적인기계적 환기법과 기관내 폐환기?
Oleic acid로 유발한 가토의 호흡부전증에서 통상적인기계적 환기법과 기관내 폐환기? 기계적 인공호흡
기계적 인공호흡 호흡부전 환자간호, 성인 호흡기 장애 증후군, 기계적 인공 호흡
호흡부전 환자간호, 성인 호흡기 장애 증후군, 기계적 인공 호흡 COPD케이스스터디
COPD케이스스터디 만성폐쇄성폐질환(COPD)의 개념, 만성폐쇄성폐질환(COPD)의 병인, 만성폐쇄성폐질환(COPD)의 ...
만성폐쇄성폐질환(COPD)의 개념, 만성폐쇄성폐질환(COPD)의 병인, 만성폐쇄성폐질환(COPD)의 ... COPD case
COPD case 경대 COPD (Chronic Obstuctive Pulmonary Disease) 만성 폐쇄성 폐질환 case study
경대 COPD (Chronic Obstuctive Pulmonary Disease) 만성 폐쇄성 폐질환 case study COPD문헌고찰
COPD문헌고찰 노화가 인체(순환기계, 호흡계, 신경계,내분비계 등)에 미치는 영향
노화가 인체(순환기계, 호흡계, 신경계,내분비계 등)에 미치는 영향 호흡기(COPD)에 대한 간호과정 - 환기관류 불균형과 관련된 가스교환 장애 & 기도분비물 ...
호흡기(COPD)에 대한 간호과정 - 환기관류 불균형과 관련된 가스교환 장애 & 기도분비물 ... COPD(Chronic Obstruction Pulmonary Disease) ; 만성 폐쇄성 폐질환에 관한 문헌고찰
COPD(Chronic Obstruction Pulmonary Disease) ; 만성 폐쇄성 폐질환에 관한 문헌고찰 ICU 에서 주로 쓰이는 진단명, 약물, 기계에 관하여 (복막염 (Peritonitis), 호흡 부전증(Res...
ICU 에서 주로 쓰이는 진단명, 약물, 기계에 관하여 (복막염 (Peritonitis), 호흡 부전증(Res... [성인간호학]호흡기내과 실습자료
[성인간호학]호흡기내과 실습자료 COPD(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) 케이스
COPD(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) 케이스





































소개글